[mythcat@desk ~]$ chmod +x krita-4.2.5-x86_64.appimage
[mythcat@desk ~]$ ./krita-4.2.5-x86_64.appimage tutorials, tips, tricks, commands, programming, linux, windows, database, sql, python, programming language, Fedora, drawing, painting, tutorial, tutorials
Wednesday, September 4, 2019
Fedora 30 : The last Krita version.
Today I will show you how to use the last version of Krita with Fedora 30 distro.
First, download the app image application Krita from the official website.
The AppImage is a format for distributing portable software on Linux without needing superuser permissions to install the application.
In the folder where is the download you need to set it executable:
Posted by
Cătălin George Feștilă
 Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
Krita,
linux,
linux tools,
tutorial,
tutorials
Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
Krita,
linux,
linux tools,
tutorial,
tutorials
Tuesday, September 3, 2019
Fedora 30 : Few commands for Fedora distro.
In this tutorial, I will show these commands for Fedora distro and what information can provide to users. First is lspci:
[root@desk mythcat]# lspci
...
05:00.1 Audio device: NVIDIA Corporation High Definition Audio Controller (rev a1)
[root@desk mythcat]# echo 1 > /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000\:0
0000:00:00.0/ 0000:00:1b.0/ 0000:00:1c.4/ 0000:00:1f.2/ 0000:05:00.0/
0000:00:02.0/ 0000:00:1c.0/ 0000:00:1d.0/ 0000:00:1f.3/ 0000:05:00.1/
0000:00:16.0/ 0000:00:1c.2/ 0000:00:1e.0/ 0000:02:00.0/
0000:00:1a.0/ 0000:00:1c.3/ 0000:00:1f.0/ 0000:03:00.0/
[root@desk mythcat]# echo 1 > /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000\:05\:00.1/remove
[root@desk mythcat]# lspci
...
05:00.0 VGA compatible controller: NVIDIA Corporation GT218 [GeForce 210] (rev a2)
[root@desk mythcat]# echo 1 > /sys/bus/pci/rescan
[root@desk mythcat]# lspci -x -s 05:00.0
05:00.0 VGA compatible controller: NVIDIA Corporation GT218 [GeForce 210] (rev a2)
00: de 10 65 0a 07 04 10 00 a2 00 00 03 01 00 80 00
10: 00 00 00 f9 0c 00 00 d0 00 00 00 00 0c 00 00 ee
20: 00 00 00 00 01 df 00 00 00 00 00 00 42 38 11 13
30: 00 00 00 00 60 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 0c 01 00 00
[root@desk mythcat]# lspci -x -s 05:00.1
05:00.1 Audio device: NVIDIA Corporation High Definition Audio Controller (rev a1)
00: de 10 e3 0b 06 00 10 00 a1 00 03 04 01 00 80 00
10: 00 00 00 fa 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
20: 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 42 38 11 13
30: 00 00 00 00 60 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 05 02 00 00[root@desk mythcat]# dmesg | grep 05:00.1
[ 0.375902] pci 0000:05:00.1: [10de:0be3] type 00 class 0x040300
[ 0.375929] pci 0000:05:00.1: reg 0x10: [mem 0xfaffc000-0xfaffffff]
[ 0.376002] pci 0000:05:00.1: enabling Extended Tags
[ 2077.961694] pci 0000:05:00.1: [10de:0be3] type 00 class 0x040300
[ 2077.961730] pci 0000:05:00.1: reg 0x10: [mem 0xfaffc000-0xfaffffff]
[ 2077.962138] pci 0000:05:00.1: BAR 0: assigned [mem 0xfa000000-0xfa003fff]
[ 2423.644523] pci 0000:05:00.1: [10de:0be3] type 00 class 0x040300
[ 2423.644559] pci 0000:05:00.1: reg 0x10: [mem 0xfa000000-0xfa003fff]
[ 2423.644968] pci 0000:05:00.1: BAR 0: assigned [mem 0xfa000000-0xfa003fff]
[ 2517.259902] pci 0000:05:00.1: [10de:0be3] type 00 class 0x040300
[ 2517.259939] pci 0000:05:00.1: reg 0x10: [mem 0xfa000000-0xfa003fff]
[ 2517.260342] pci 0000:05:00.1: BAR 0: assigned [mem 0xfa000000-0xfa003fff][root@desk mythcat]# echo 1 > /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:05:00.1/remove
[root@desk mythcat]# lspci -x -s 05:00.1
[root@desk mythcat]# [root@desk mythcat]# lspci -v | grep -A7 -i "audio"
00:1b.0 Audio device: Intel Corporation 6 Series/C200 Series Chipset Family High Definition Audio
Controller (rev 05)
Subsystem: Gigabyte Technology Co., Ltd Device a002
Flags: bus master, fast devsel, latency 0, IRQ 3
Memory at fbff4000 (64-bit, non-prefetchable) [size=16K]
Capabilities: [50] Power Management version 2
Capabilities: [60] MSI: Enable- Count=1/1 Maskable- 64bit+
Capabilities: [70] Express Root Complex Integrated Endpoint, MSI 00
Capabilities: [100] Virtual Channel
--
05:00.1 Audio device: NVIDIA Corporation High Definition Audio Controller (rev a1)
Subsystem: eVga.com. Corp. Device 1311
Flags: bus master, fast devsel, latency 0, IRQ 5
Memory at faffc000 (32-bit, non-prefetchable) [size=16K]
Capabilities: [60] Power Management version 3
Capabilities: [68] MSI: Enable- Count=1/1 Maskable- 64bit+
Capabilities: [78] Express Endpoint, MSI 00
[root@desk mythcat]# systemctl status alsa-state.service
● alsa-state.service - Manage Sound Card State (restore and store)
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/alsa-state.service; static; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
[root@desk mythcat]# systemctl start alsa-state.service
[root@desk mythcat]# systemctl status alsa-state.service
● alsa-state.service - Manage Sound Card State (restore and store)
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/alsa-state.service; static; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2019-08-29 13:53:58 EEST; 1s ago
Main PID: 2951 (alsactl)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 1942)
Memory: 1.3M
CGroup: /system.slice/alsa-state.service
└─2951 /usr/sbin/alsactl -s -n 19 -c -E ALSA_CONFIG_PATH=/etc/alsa/alsactl.conf
--initfile=/lib/alsa/init/00main >
Aug 29 13:53:58 desk systemd[1]: Started Manage Sound Card State (restore and store).
Aug 29 13:53:58 desk alsactl[2951]: alsactl 1.1.9 daemon started
Aug 29 13:53:58 desk alsactl[2951]: /usr/sbin/alsactl: load_state:1735No soundcards found...
[root@desk mythcat]# systemctl status alsa-restore.service
● alsa-restore.service - Save/Restore Sound Card State
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/alsa-restore.service; static; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
[root@desk mythcat]# systemctl start alsa-restore.service
[root@desk mythcat]# systemctl status alsa-restore.service
● alsa-restore.service - Save/Restore Sound Card State
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/alsa-restore.service; static; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
Aug 29 13:58:53 desk systemd[1]: Condition check resulted in Save/Restore Sound Card State being skipped.[root@desk mythcat]# hostnamectl set-hostname new_hostname[root@desk mythcat]# dnf
Posted by
Cătălin George Feștilă
 Labels:
2019,
bus,
dmesg,
dnf,
echo,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
hostnamectl,
linux,
linux tools,
lspci,
systemctl,
tutorial,
tutorials
Labels:
2019,
bus,
dmesg,
dnf,
echo,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
hostnamectl,
linux,
linux tools,
lspci,
systemctl,
tutorial,
tutorials
Saturday, August 31, 2019
Fedora 30 : Rollback to Fedora 30.
In this tutorial, I will show you how to rollback from a bad distro update of Fedora 31 to the old one Fedora 30.
If you follow this tutorial and you got errors then your dnf tool will have problems with update process.
After I follow the tutorial I got many packages and errors.
I try to fix with this but not work:
The option of dnf tool clean all --releasever=32 will clean all packages from fc32.
I used this command to see what packages with errors and the repo with problems:
If you follow this tutorial and you got errors then your dnf tool will have problems with update process.
After I follow the tutorial I got many packages and errors.
I try to fix with this but not work:
[root@desk mythcat]# dnf system-upgrade download --refresh --releasever=31
--setopt=module_platform_id=platform:f31 --skip-broken
Before you continue to ensure that your system is fully upgraded by running "dnf
--refresh upgrade". Do you want to continue [y/N]: y
...[root@desk mythcat]# pkcon refresh force -c -1
[root@desk mythcat]# dnf --releasever=30 --allowerasing downgrade fedora
[root@desk mythcat]# dnf clean all --releasever=32
[root@desk mythcat]# dnf clean all --releasever=31
[root@desk mythcat]# dnf clean all --releasever=30The option of dnf tool clean all --releasever=32 will clean all packages from fc32.
I used this command to see what packages with errors and the repo with problems:
[root@desk mythcat]# dnf --releasever=30 --allowerasing downgrade fedora
...[root@desk mythcat]# ls -l /etc/yum.repos.d/
[root@desk mythcat]# rm /etc/yum.repos.d/fedora-rawhide.repo
[root@desk mythcat]# rm /etc/yum.repos.d/fedora-rawhide-modular.repo Friday, August 30, 2019
Fedora 30 : DNF history.
This option of the tool DNF can help you to see and rollback by transaction history.
NOTE: This option not work if you use the system-upgrade to another version of the distro.
[root@desk mythcat]# dnf
usage: dnf [options] COMMAND
List of Main Commands:
...
history display, or use, the transaction history
... [root@desk mythcat]# dnf history
ID | Command line | Date and time | Action(s) | Altered
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
64 | groupupdate Minimal Inst | 2019-08-29 21:59 | Install | 2
63 | groupupdate Minimal Inst | 2019-08-29 21:59 | Install | 2
[root@desk mythcat]# dnf history info 64
Transaction ID : 64
Begin time : Thu 29 Aug 2019 09:59:52 PM EEST
Begin rpmdb : 1643:6a997d9fa53488ec0003727cb0394b18b6b4deaf
End time : Thu 29 Aug 2019 09:59:53 PM EEST (1 seconds)
End rpmdb : 1643:6a997d9fa53488ec0003727cb0394b18b6b4deaf
User : Catalin George Festila
Return-Code : Success
Releasever : 30
Command Line : groupupdate Minimal Install
Packages Altered:
Install @core
Install @minimal-environment
[root@desk mythcat]# dnf history undo 64
Posted by
Cătălin George Feștilă
 Labels:
2019,
dnf,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
linux,
linux tools,
tutorial,
tutorials
Labels:
2019,
dnf,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
linux,
linux tools,
tutorial,
tutorials
Thursday, August 22, 2019
Fedora 30 : Set up the Linux Malware Detect.
If you have an SELinux warning detection then the details you can see how can be fixed:
These modes are USERS|PATHS|FILES.
The options break down as follows:
[mythcat@desk ~]$ su
Password:
[root@desk mythcat]# ausearch -c 'systemd' --raw | audit2allow -M my-systemd
******************** IMPORTANT ***********************
To make this policy package active, execute:
semodule -i my-systemd.pp
[root@desk mythcat]# semodule -X 300 -i my-systemd.ppThese modes are USERS|PATHS|FILES.
The options break down as follows:
- USERS: The users option will take the homedirs of all system users that are above inotify_minuid and monitor them.If inotify_webdir is set then the users webdir, if it exists, will only be monitored;
- PATHS: A comma spaced list of paths to monitor;
- FILE: A line spaced file list of paths to monitor
$ maldet --monitor users
$ maldet --monitor /root/initial-setup-ks.cfg
$ maldet --monitor /home/mythcat[mythcat@desk maldetect-1.6.4]$ maldet --monitor users
Linux Malware Detect v1.6.4
(C) 2002-2019, R-fx Networks
(C) 2019, Ryan MacDonald
This program may be freely redistributed under the terms of the GNU GPL v2
maldet(7958): {mon} could not find inotifywait command, install yum package inotify-tools or download from https://github.com/rvoicilas/inotify-tools/wiki/
[root@desk maldetect-1.6.4]# dnf search inotify-tools
Last metadata expiration check: 0:01:39 ago on Wed 21 Aug 2019 11:09:22 PM EEST.
============================================ Name Exactly Matched: inotify-tools ======
inotify-tools.i686 : Command line utilities for inotify
inotify-tools.x86_64 : Command line utilities for inotify
================================================ Name Matched: inotify-tools ======
inotify-tools-devel.i686 : Headers and libraries for building apps that use libinotifytools
inotify-tools-devel.x86_64 : Headers and libraries for building apps that use libinotifytools
[root@desk maldetect-1.6.4]# dnf install inotify-tools.x86_64
...
Installed:
inotify-tools-3.14-16.fc30.x86_64
Complete!
[root@desk maldetect-1.6.4]# maldet --monitor users
Linux Malware Detect v1.6.4
(C) 2002-2019, R-fx Networks
(C) 2019, Ryan MacDonald
This program may be freely redistributed under the terms of the GNU GPL v2
maldet(973): {mon} set inotify max_user_watches to 16384
maldet(973): {mon} added /dev/shm to inotify monitoring array
maldet(973): {mon} added /var/tmp to inotify monitoring array
maldet(973): {mon} added /tmp to inotify monitoring array
maldet(973): {mon} starting inotify process on 3 paths, this might take awhile...
maldet(973): {mon} inotify startup successful (pid: 1800)
maldet(973): {mon} inotify monitoring log: /usr/local/maldetect/logs/inotify_log
Posted by
Cătălin George Feștilă
 Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
internet security,
linux,
linux tools,
malware,
security,
selinux,
tutorial,
tutorials
Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
internet security,
linux,
linux tools,
malware,
security,
selinux,
tutorial,
tutorials
Wednesday, August 21, 2019
Fedora 30 : Testing the Linux Malware Detect.
Linux Malware Detect (LMD) is a malware scanner for Linux released under the GNU GPLv2 license, that is designed around the threats faced in shared hosted environments.
This tool is provided by R-fx Networks.
Let's install and test it:
Now you can run it:
This tool is provided by R-fx Networks.
Let's install and test it:
[mythcat@desk ~]$ wget http://www.rfxn.com/downloads/maldetect-current.tar.gz
[mythcat@desk ~]$ tar -xf maldetect-current.tar.gz
[mythcat@desk ~]$ cd maldetect-1.6.4/
[mythcat@desk maldetect-1.6.4]$ su
Password:
[root@desk maldetect-1.6.4]# ./install.sh
Failed to enable unit: Unit file maldet.service does not exist.
Linux Malware Detect v1.6.4
(C) 2002-2019, R-fx Networks <proj@r-fx.org>
(C) 2019, Ryan MacDonald <ryan@r-fx.org>
This program may be freely redistributed under the terms of the GNU GPL
installation completed to /usr/local/maldetect
config file: /usr/local/maldetect/conf.maldet
exec file: /usr/local/maldetect/maldet
exec link: /usr/local/sbin/maldet
exec link: /usr/local/sbin/lmd
cron.daily: /etc/cron.daily/maldet
maldet(31046): {sigup} performing signature update check...
maldet(31046): {sigup} local signature set is version 201907043616
maldet(31046): {sigup} new signature set 2019081912001 available
maldet(31046): {sigup} downloading https://cdn.rfxn.com/downloads/maldet-sigpack.tgz
maldet(31046): {sigup} downloading https://cdn.rfxn.com/downloads/maldet-cleanv2.tgz
maldet(31046): {sigup} verified md5sum of maldet-sigpack.tgz
maldet(31046): {sigup} unpacked and installed maldet-sigpack.tgz
maldet(31046): {sigup} verified md5sum of maldet-clean.tgz
maldet(31046): {sigup} unpacked and installed maldet-clean.tgz
maldet(31046): {sigup} signature set update completed
maldet(31046): {sigup} 15552 signatures (12740 MD5 | 2035 HEX | 777 YARA | 0 USER)
[root@desk maldetect-1.6.4]# vim /usr/local/maldetect/conf.maldetNow you can run it:
[mythcat@desk ~]$ /usr/local/sbin/maldet -a
Linux Malware Detect v1.6.4
(C) 2002-2019, R-fx Networks
(C) 2019, Ryan MacDonald
This program may be freely redistributed under the terms of the GNU GPL v2
maldet(32628): {scan} signatures loaded: 15552 (12740 MD5 | 2035 HEX | 777 YARA | 0 USER)
maldet(32628): {scan} building file list for , this might take awhile...
maldet(32628): {scan} setting nice scheduler priorities for all operations: cpunice 19 , ionice 6
maldet(32628): {scan} file list completed in 13s, found 44109 files...
maldet(32628): {scan} scan of (44109 files) in progress...
Posted by
Cătălin George Feștilă
 Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
internet security,
linux,
linux tools,
malware,
security,
tutorial,
tutorials
Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
internet security,
linux,
linux tools,
malware,
security,
tutorial,
tutorials
Tuesday, August 20, 2019
Fedora 30 : Install the last version of PHP.
I try to install the last version of PHP version 7.4.0beta2 with Fedora 30 distro the LXQt environment.
I have not used this programming language for a few years and it is a good issue to remember it.
I download teh archive from the official website and I run these commands:
I have not used this programming language for a few years and it is a good issue to remember it.
I download teh archive from the official website and I run these commands:
[mythcat@desk ~]$ cd php/
[mythcat@desk php]$ tar -xf php-7.4.0beta2.tar.xz
[mythcat@desk php]$ cd php-7.4.0beta2/
[mythcat@desk php-7.4.0beta2]$ ./configure --prefix=$HOME/local
checking for grep that handles long lines and -e... /usr/bin/grep
checking for egrep... /usr/bin/grep -E
checking for a sed that does not truncate output... /usr/bin/sed
checking build system type... x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
checking host system type... x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
checking target system type... x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
checking for pkg-config... /usr/bin/pkg-config
checking pkg-config is at least version 0.9.0... yes
checking for cc... no
checking for gcc... no
configure: error: in `/home/mythcat/php/php-7.4.0beta2':
configure: error: no acceptable C compiler found in $PATH
See `config.log' for more details
[mythcat@desk php-7.4.0beta2]$ vi config
[mythcat@desk php-7.4.0beta2]$ vi config
config.log config.nice configure configure.ac
[mythcat@desk php-7.4.0beta2]$ vi config.log [root@desk home]# dnf groupinstall "Development Tools"[root@desk home]# dnf groupinstall "Development Tools"
Waiting for process with pid 4373 to finish.
[root@desk home]# kill -9 4373
[root@desk home]# dnf groupinstall "Development Tools"
...
Complete!
[root@desk home]# dnf install libxml2-devel.x86_64
...
Installed:
libxml2-devel-2.9.9-2.fc30.x86_64 xz-devel-5.2.4-5.fc30.x86_64
checking for sqlite3 > 3.7.4... no
configure: error: Package requirements (sqlite3 > 3.7.4) were not met:
Package 'sqlite3', required by 'virtual:world', not found
Consider adjusting the PKG_CONFIG_PATH environment variable if you
installed software in a non-standard prefix. [root@desk home]# dnf install sqlite-devel.x86_64
...
Installed:
sqlite-devel-3.26.0-6.fc30.x86_64 [mythcat@desk php-7.4.0beta2]$ ./configure --prefix=$HOME/local
...
config.status: executing default commands
+--------------------------------------------------------------------+
| License: |
| This software is subject to the PHP License, available in this |
| distribution in the file LICENSE. By continuing this installation |
| process, you are bound by the terms of this license agreement. |
| If you do not agree with the terms of this license, you must abort |
| the installation process at this point. |
+--------------------------------------------------------------------+
Thank you for using PHP.
[mythcat@desk php-7.4.0beta2]$ make
...
Build complete.
Don't forget to run 'make test'.
[mythcat@desk php-7.4.0beta2]$ make install
...
[mythcat@desk php-7.4.0beta2]$ make test
...
FAILED TEST SUMMARY
---------------------------------------------------------------------
php://fd wrapper: invalid file descriptor [ext/standard/tests/file/php_fd_wrapper_04.phpt]
=====================================================================
You may have found a problem in PHP.
This report can be automatically sent to the PHP QA team at
http://qa.php.net/reports and http://news.php.net/php.qa.reports
This gives us a better understanding of PHP's behavior.
If you don't want to send the report immediately you can choose
option "s" to save it. You can then email it to qa-reports@lists.php.net later.
Do you want to send this report now? [Yns]: s
sh: autoconf: command not found
Please send /home/mythcat/php/php-7.4.0beta2/php_test_results_20190819_2038.txt to qa-reports@lists.php.net
manually, thank you.
make: *** [Makefile:201: test] Error 1
[mythcat@desk php-7.4.0beta2]$ export PATH=$HOME/local/bin:$PATH
[mythcat@desk php-7.4.0beta2]$ . ~/.bash_profile
[mythcat@desk php-7.4.0beta2]$ which php
~/local/bin/php
[mythcat@desk php-7.4.0beta2]$ php -v
PHP 7.4.0beta2 (cli) (built: Aug 19 2019 23:31:07) ( NTS )
Copyright (c) The PHP Group
Zend Engine v3.4.0-dev, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies[mythcat@desk php-7.4.0beta2]$ php -i | grep 'API'
Server API => Command Line Interface
PHP API => 20190529
Zend Extension Build => API320190529,NTS
PHP Extension Build => API20190529,NTS
DOM/XML API Version => 20031129
Phar API version => 1.1.1
[mythcat@desk php-7.4.0beta2]$ echo '' > infophp.php
[mythcat@desk php-7.4.0beta2]$ php -f infophp.php
phpinfo()
PHP Version => 7.4.0beta2
System => Linux desk 5.2.8-200.fc30.x86_64 #1 SMP Sat Aug 10 13:21:39 UTC 2019 x86_64
Build Date => Aug 19 2019 23:26:58
Configure Command => './configure' '--prefix=/home/mythcat/local'
Server API => Command Line Interface
Virtual Directory Support => disabled
...[mythcat@desk php-7.4.0beta2]$ php -a
Interactive mode enabled
hello, world1636562552[mythcat@desk php-7.4.0beta2]$ php -m
[PHP Modules]
Core
ctype
date
dom
fileinfo
filter
hash
iconv
json
libxml
pcre
PDO
pdo_sqlite
Phar
posix
Reflection
session
SimpleXML
SPL
sqlite3
standard
tokenizer
xml
xmlreader
xmlwriter
[Zend Modules]
Posted by
Cătălin George Feștilă
 Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
linux,
linux tools,
php,
tutorial,
tutorials,
web development
Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
linux,
linux tools,
php,
tutorial,
tutorials,
web development
Friday, August 16, 2019
Fedora 30 : First steps with Fedora and GitHub.
In this tutorial I will show you how you can use Fedora and your GitHub account for your projects.
Let's solve this issue in a simple way.
First, you need to install the git tool with dnf tool:
Let's solve this issue in a simple way.
First, you need to install the git tool with dnf tool:
[root@desk mythcat]# dnf -y install git[mythcat@desk ~]$ git --version
git version 2.21.0[mythcat@desk ~]$ git config --global user.name "catafest"
[mythcat@desk ~]$ git config --global user.email "catafest@yahoo.com"[mythcat@desk ~]$ git config --list
[mythcat@desk ~]$ git config --global --list[mythcat@desk ~]$ mkdir project_github
[mythcat@desk ~]$ cd project_github/ [mythcat@desk project_github]$ git clone https://github.com/catafest/flask_yt.git
Cloning into 'flask_yt'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 23, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (23/23), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (19/19), done.
remote: Total 23 (delta 1), reused 14 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
Unpacking objects: 100% (23/23), done.
[mythcat@desk project_github]$ cd flask_yt/
[mythcat@desk flask_yt]$ vim README.md
...[mythcat@desk flask_yt]$ git status
On branch master
Your branch is up to date with 'origin/master'.
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add ..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git checkout -- ..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: README.md
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
[mythcat@desk flask_yt]$ git add *
[mythcat@desk flask_yt]$ git commit -m "first commit"
[master 56f1e53] first commit
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) [mythcat@desk flask_yt]$ git push origin master
Enumerating objects: 5, done.
Counting objects: 100% (5/5), done.
Delta compression using up to 2 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 352 bytes | 352.00 KiB/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0)
remote: Resolving deltas: 100% (1/1), completed with 1 local object.
To https://github.com/catafest/flask_yt.git
5ecffdd..56f1e53 master -> master
Posted by
Cătălin George Feștilă
 Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
git,
GitHub,
linux,
linux tools,
tutorial,
tutorials
Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
git,
GitHub,
linux,
linux tools,
tutorial,
tutorials
Wednesday, August 14, 2019
Fedora 30 : First steps with Fedora firewall.
In computing, a firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.[1] A firewall typically establishes a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external network, such as the Internet.[2], see the wikipedia.
In this short tutorial about the Fedora firewall subject, I will show you how you can use firewall commands to set it.
The install is simple with dnf tool:
[root@desk mythcat]# dnf install firewalld firewall-config [root@desk mythcat]# systemctl status firewalld
● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon
...
[root@desk mythcat]# systemctl start firewalld
[root@desk mythcat]# systemctl restart firewalld
[root@desk mythcat]# systemctl stop firewalld[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --get-active-zones[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-all[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports [root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp
[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --remove-port=80/tcp[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --get-services
RH-Satellite-6 amanda-client amanda-k5-client amqp amqps apcupsd audit bacula bacula-client
bgp bitcoin bitcoin-rpc bitcoin-testnet bitcoin-testnet-rpc ceph ceph-mon cfengine cockpit
condor-collector ctdb dhcp dhcpv6 dhcpv6-client distcc dns docker-registry docker-swarm
dropbox-lansync elasticsearch etcd-client etcd-server finger freeipa-ldap freeipa-ldaps
freeipa-replication freeipa-trust ftp ganglia-client ganglia-master git gre high-availability
http https imap imaps ipp ipp-client ipsec irc ircs iscsi-target isns jenkins kadmin kerberos
kibana klogin kpasswd kprop kshell ldap ldaps libvirt libvirt-tls lightning-network llmnr
managesieve matrix mdns minidlna mongodb mosh mountd mqtt mqtt-tls ms-wbt mssql murmur mysql
nfs nfs3 nmea-0183 nrpe ntp nut openvpn ovirt-imageio ovirt-storageconsole ovirt-vmconsole
plex pmcd pmproxy pmwebapi pmwebapis pop3 pop3s postgresql privoxy proxy-dhcp ptp pulseaudio
puppetmaster quassel radius redis rpc-bind rsh rsyncd rtsp salt-master samba samba-client
samba-dc sane sip sips slp smtp smtp-submission smtps snmp snmptrap spideroak-lansync squid
ssh steam-streaming svdrp svn syncthing syncthing-gui synergy syslog syslog-tls telnet tftp
tftp-client tinc tor-socks transmission-client upnp-client vdsm vnc-server wbem-http
wbem-https wsman wsmans xdmcp xmpp-bosh xmpp-client xmpp-local xmpp-server zabbix-agent
zabbix-server[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=ftp
[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-service=ftp[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-services[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --panic-on
[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --panic-off [root@desk mythcat]# ping google.com -c 1
[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --query-panic
[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --panic-off[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --zone=external --query-masquerade[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-forward-port=port=80:proto=tcp:toaddr=6.6.6.6[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --get-icmptypes
address-unreachable bad-header beyond-scope communication-prohibited destination-unreachable
echo-reply echo-request failed-policy fragmentation-needed host-precedence-violation
host-prohibited host-redirect host-unknown host-unreachable ip-header-bad
neighbour-advertisement neighbour-solicitation network-prohibited network-redirect
network-unknown network-unreachable no-route packet-too-big parameter-problem
port-unreachable precedence-cutoff protocol-unreachable redirect reject-route
required-option-missing router-advertisement router-solicitation source-quench
source-route-failed time-exceeded timestamp-reply timestamp-request tos-host-redirect
tos-host-unreachable tos-network-redirect tos-network-unreachable
ttl-zero-during-reassembly ttl-zero-during-transit unknown-header-type
unknown-option[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --zone=external --query-icmp-block=echo-reply
[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --zone=external --add-icmp-block=echo-reply[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --direct --get-rules ipv4 filter IN_public
[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-cmd --direct --add-rule ipv4 filter IN_public_allow
...[root@desk mythcat]# firewall-config
Posted by
Cătălin George Feștilă
 Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
firewall,
internet security,
linux,
linux tools,
security,
tutorial,
tutorials
Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
firewall,
internet security,
linux,
linux tools,
security,
tutorial,
tutorials
Monday, August 12, 2019
Fedora 30 : First step with Ionic.
My laptop is crash and is hard for me to write tutorials for me.
The last tutorial I created with Fedora 30 is about Ionic.
You can read this tutorial here.
The last tutorial I created with Fedora 30 is about Ionic.
You can read this tutorial here.
Posted by
Cătălin George Feștilă
 Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
Ionic,
linux,
programming,
tutorial,
tutorials,
web development
Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
Ionic,
linux,
programming,
tutorial,
tutorials,
web development
Friday, August 9, 2019
Fedora 30 : The VS Code on Fedora.
The Visual Studio Code editor is officially distributed as a Snap package in the Snap Store.
It runs well on the Fedora distro, but with my Window operating system is crash often.
I like to develop my python projects like Flask and Django with this editor.
You can install it very easy on Fedora with the dnf tool:
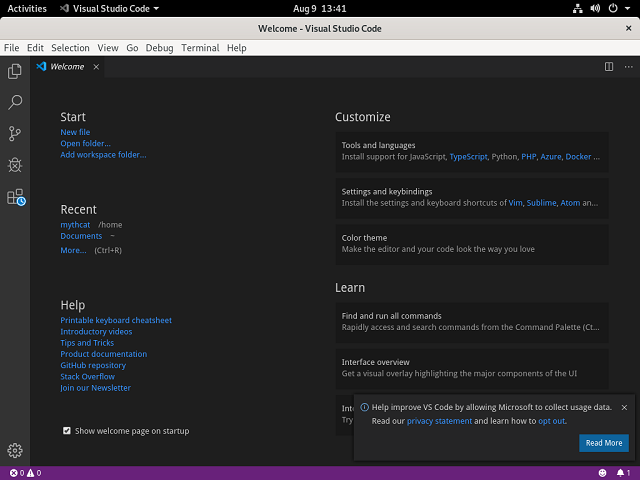
The result of my installation on Fedora 30 distro can be seen at this screenshot:
It runs well on the Fedora distro, but with my Window operating system is crash often.
I like to develop my python projects like Flask and Django with this editor.
You can install it very easy on Fedora with the dnf tool:
[mythcat@desk ~]# dnf check-update
[mythcat@desk ~]# dnf update
[mythcat@desk ~]# exit
[mythcat@desk ~]$ sudo dnf install code
[sudo] password for mythcat:
...
Is this ok [y/N]: y
...
Installed:
code-1.37.0-1565228125.el7.x86_64sudo snap install --classic code[mythcat@desk ~]$ codeThe result of my installation on Fedora 30 distro can be seen at this screenshot:

Posted by
Cătălin George Feștilă
 Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
IDE,
linux,
linux tools,
Microsoft,
programming,
tutorial,
tutorials,
Visual Studio
Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
IDE,
linux,
linux tools,
Microsoft,
programming,
tutorial,
tutorials,
Visual Studio
Tuesday, August 6, 2019
Fedora 30 : The gpg tool.
GnuPG allows you to encrypt and sign your data and communications; it features a versatile key management system, along with access modules for all kinds of public key directories. see the official webpage.
Today I test it with Fedora 30 distro and works well.
You can find this tool in many Linux distros.
Let's install it with dnf tool.
Today I test it with Fedora 30 distro and works well.
You can find this tool in many Linux distros.
Let's install it with dnf tool.
[root@desk mythcat]# dnf install gnupg
Last metadata expiration check: 0:18:30 ago on Tue 06 Aug 2019 11:07:20 AM EEST.
Package gnupg2-2.2.17-1.fc30.x86_64 is already installed.
Dependencies resolved.
Nothing to do.
Complete!
[root@desk mythcat]# exit
exit[mythcat@desk ~]$ gpg --list-secret-keys
[mythcat@desk ~]$ gpg --list-keys
[mythcat@desk ~]$ gpg --full-generate-key
gpg (GnuPG) 2.2.17; Copyright (C) 2019 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
Please select what kind of key you want:
(1) RSA and RSA (default)
(2) DSA and Elgamal
(3) DSA (sign only)
(4) RSA (sign only)
Your selection?
Your selection? 1
RSA keys may be between 1024 and 4096 bits long.
What keysize do you want? (2048)
Requested keysize is 2048 bits
Please specify how long the key should be valid.
0 = key does not expire
= key expires in n days
w = key expires in n weeks
m = key expires in n months
y = key expires in n years
Key is valid for? (0) 0
Key does not expire at all
Is this correct? (y/N) y
GnuPG needs to construct a user ID to identify your key.
Real name: Catalin George Festila
Email address: catafest@yahoo.com
Comment: test gpg key
You selected this USER-ID:
...
Change (N)ame, (C)omment, (E)mail or (O)kay/(Q)uit? O
Enter password for protection
We need to generate a lot of random bytes. It is a good idea to perform
some other action (type on the keyboard, move the mouse, utilize the
disks) during the prime generation; this gives the random number
generator a better chance to gain enough entropy.
...
[mythcat@desk ~]$ gpg --gen-key
gpg (GnuPG) 2.2.17; Copyright (C) 2019 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
Note: Use "gpg --full-generate-key" for a full featured key generation dialog.
GnuPG needs to construct a user ID to identify your key.
Real name:
... [mythcat@desk ~]$ gpg --list-keys
/home/mythcat/.gnupg/pubring.kbx
--------------------------------[mythcat@desk ~]$ gpg --output mythcat --export catafest@yahoo.com[mythcat@desk ~]$ gpg --armor --export catafest@yahoo.com > catafest.key[mythcat@desk ~]$ cat catafest.key
...[mythcat@desk ~]$ gpg --list-keys
/home/mythcat/.gnupg/pubring.kbx
-------------------------------- [mythcat@desk ~]$ gpg --edit-key catafest@yahoo.com
gpg (GnuPG) 2.2.17; Copyright (C) 2019 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
Secret key is available.
...
gpg> ?
quit quit this menu
save save and quit
help show this help
fpr show key fingerprint
grip show the keygrip
...
enable enable key
disable disable key
showphoto show selected photo IDs
clean compact unusable user IDs and remove unusable signatures from key
minimize compact unusable user IDs and remove all signatures from key
...[mythcat@desk ~]$ gpg --export -a catafest > catafest_public.key
[mythcat@desk ~]$ gpg --import -a catafest_public.key
...
gpg: Total number processed: 1
gpg: unchanged: 1[mythcat@desk ~]$ echo "test gpg encrypt" >> gpgtest.txt
[mythcat@desk ~]$ gpg -e -r "catafest" gpgtest.txt
[mythcat@desk ~]$ gpg -d gpgtest.txt.gpg
...
test gpg encrypt[mythcat@desk ~]$ gpg --export --armor --output catafest.asc catafest@yahoo.com
[mythcat@desk ~]$ gpg --import catafest.asc
...
gpg: Total number processed: 1
gpg: unchanged: 1
[mythcat@desk ~]$ echo "this text will be encrypt and decrypt" | gpg --passphrase-file catafest.asc
--batch --symmetric --cipher-algo AES256 > testgpg_001.txt
[mythcat@desk ~]$ gpg --batch --passphrase-file catafest.asc -d testgpg_001.txt
gpg: AES256 encrypted data
gpg: encrypted with 1 passphrase
this text will be encrypt and decrypt
Posted by
Cătălin George Feștilă
 Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
GnuPG,
gpg,
linux,
linux tools,
tutorial,
tutorials
Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
GnuPG,
gpg,
linux,
linux tools,
tutorial,
tutorials
Monday, July 8, 2019
Fedora 30 : Using the python-wikitcms.
This python module named python-wikitcms can be used for interacting with the Fedora wiki.
The Fedora wiki used Fedora's Wikitcms.
Today I test it and works great with Fedora distro version 30.
First, the install of the fedora package with DNF tool:
The OpenID Connect client Wiki Test Control Management System is asking to authorize access for mythcat. this allow you to access it
After I agree with this the page tells me to close it:
You can close this window and return to the CLI
The next examples show you how to get and show information from the wiki:
The Fedora wiki used Fedora's Wikitcms.
Today I test it and works great with Fedora distro version 30.
First, the install of the fedora package with DNF tool:
[root@desk mythcat]# dnf install python3-wikitcms.noarch
...
Downloading Packages:
(1/8): python3-mwclient-0.9.3-3.fc30.noarch.rpm 186 kB/s | 61 kB 00:00
(2/8): python3-fedfind-4.2.5-1.fc30.noarch.rpm 314 kB/s | 105 kB 00:00
(3/8): python3-cached_property-1.5.1-3.fc30.noa 41 kB/s | 20 kB 00:00
(4/8): python3-requests-oauthlib-1.0.0-1.fc29.n 313 kB/s | 40 kB 00:00
(5/8): python3-jwt-1.7.1-2.fc30.noarch.rpm 112 kB/s | 42 kB 00:00
(6/8): python3-oauthlib-2.1.0-1.fc29.noarch.rpm 293 kB/s | 153 kB 00:00
(7/8): python3-simplejson-3.16.0-2.fc30.x86_64. 641 kB/s | 278 kB 00:00
(8/8): python3-wikitcms-2.4.2-2.fc30.noarch.rpm 264 kB/s | 84 kB 00:00[mythcat@desk ~]$ python3
Python 3.7.3 (default, May 11 2019, 00:38:04)
[GCC 9.1.1 20190503 (Red Hat 9.1.1-1)] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> from wikitcms.wiki import Wiki
>>> my_site = Wiki()
>>> event = my_site.current_event
>>> print(event.version)
31 Rawhide 20190704.n.1
>>> page = my_site.get_validation_page('Installation','23','Final','RC10')
>>> for row in page.get_resultrows():
... print(row.testcase)
...
QA:Testcase_Mediakit_Checksums
QA:Testcase_Mediakit_ISO_Size
QA:Testcase_Mediakit_Repoclosure
QA:Testcase_Mediakit_FileConflicts
QA:Testcase_Boot_default_install
...
>>> dir(my_site)>>> my_site.login()The OpenID Connect client Wiki Test Control Management System is asking to authorize access for mythcat. this allow you to access it
After I agree with this the page tells me to close it:
You can close this window and return to the CLI
The next examples show you how to get and show information from the wiki:
>>> print(my_site.username)
Mythcat
>>> result = my_site.api('query', titles='Mythcat')
>>> for page in result['query']['pages'].values():
... print(page['title'])
...
Mythcat
>>> for my_contributions in my_site.usercontributions('Mythcat'):
... print(my_contributions)
...
Posted by
Cătălin George Feștilă
 Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
linux,
linux tools,
module,
python,
python 3,
python modules,
python-wikitcms,
tutorial,
tutorials
Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
linux,
linux tools,
module,
python,
python 3,
python modules,
python-wikitcms,
tutorial,
tutorials
Sunday, June 30, 2019
Fedora 30 : The Pythonic tool.
The tutorial for today is about Pythonic tool.
Named Pythonic is a graphical programming tool that makes it easy for users to create Python applications using ready-made function modules.
This tool providing the consistent features and characteristics of a trading bot with just a few clicks.
The Pythonic tool is currently available in four languages: English, German, Spanish, and Chinese.
The tool comes with basic functions such as a scheduler, if-branches, connectivity, and logging functions are available out of the box and can be parameterized using a corresponding GUI.
Each graphical element is functionally processed individually.
The base idea is: A unique graphical input mask to carry out the parameterization necessary for processing, then after a process completes successfully, the returned result can be transferred to a subsequent process for further use.
You can use server processes can be placed in parallel in the background as listener applications that wait for external events and initiate the creation of a process when the event arrives.
Pythonic's data type list makes it easy to utilize different access techniques (push, pop, insert, append).
The install of this tool is easy on Fedora 30 distro:

Named Pythonic is a graphical programming tool that makes it easy for users to create Python applications using ready-made function modules.
This tool providing the consistent features and characteristics of a trading bot with just a few clicks.
The Pythonic tool is currently available in four languages: English, German, Spanish, and Chinese.
The tool comes with basic functions such as a scheduler, if-branches, connectivity, and logging functions are available out of the box and can be parameterized using a corresponding GUI.
Each graphical element is functionally processed individually.
The base idea is: A unique graphical input mask to carry out the parameterization necessary for processing, then after a process completes successfully, the returned result can be transferred to a subsequent process for further use.
You can use server processes can be placed in parallel in the background as listener applications that wait for external events and initiate the creation of a process when the event arrives.
Pythonic's data type list makes it easy to utilize different access techniques (push, pop, insert, append).
The install of this tool is easy on Fedora 30 distro:
[mythcat@desk ~]$ python3.7 -m pip install Pythonic --user
Collecting Pythonic
...
Successfully installed PyQt5-5.8.2 Pythonic-0.12 pandas-0.24.2 pythonic-binance-0.7.2
Posted by
Cătălin George Feștilă
 Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
linux,
linux tools,
module,
python,
python 3,
python modules,
Pythonic,
tutorial,
tutorials
Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
linux,
linux tools,
module,
python,
python 3,
python modules,
Pythonic,
tutorial,
tutorials
Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Fedora 30 : About HTTPie.
From the official website we can get this info about this tool.
HTTPie consists of a single http command designed for painless debugging and interaction with
HTTPie consists of a single http command designed for painless debugging and interaction with
- HTTP servers, RESTful APIs, and web services:
- Sensible defaults;
- Expressive and intuitive command syntax;
- Colorized and formatted terminal output;
- Built-in JSON support;
- Persistent sessions;
- Forms and file uploads;
- HTTPS, proxies, and authentication support;
- Support for arbitrary request data and headers;
- Wget-like downloads;
- Extensions;
- Linux, macOS, and Windows support;
- And more…
[root@desk mythcat]# dnf install httpie
...
Installed:
httpie-0.9.4-13.fc30.noarch python3-pygments-2.2.0-16.fc30.noarch [mythcat@desk ~]$ http httpie.org
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
CF-RAY: 4e18f3613c36acf4-OTP
Cache-Control: max-age=3600
Connection: keep-alive
Date: Tue, 04 Jun 2019 09:41:22 GMT
Expires: Tue, 04 Jun 2019 10:41:22 GMT
Location: https://httpie.org/
Server: cloudflare
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Vary: Accept-Encoding
Posted by
Cătălin George Feștilă
 Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
HTTPie,
linux,
linux tools,
tutorial,
tutorials
Labels:
2019,
Fedora,
Fedora 30,
HTTPie,
linux,
linux tools,
tutorial,
tutorials
Tuesday, May 28, 2019
Fedora 30 : Commands and tools that handle assembly files - part 002.
Another good approach to this topic is this Fedora tool.
The development team tells us: GNUSim8085 is a graphical simulator, assembler and debugger for the Intel 8085 microprocessor in Linux and Windows.
The Intel 8085 has seven internal general-purpose 8-bit registers A, B, C, D, E, H, L, and 5 flags — S (sign), Z (zero), AC (Aux Carry), P (Parity) and CY (Carry).
The processor has a total of 246 instructions with which we can manipulate data in the processor registers and memory.
The assembler Intel 8085 mnemonics with the instruction strings, labels define with a named point in the code, the target for JMP or CALL instructions, comments start line with a semicolon ‘;’ is ignored by the assembler and pseudo codes to the assembler that provides some features to the coding process.
For another development assembly tools for hardware, you can find more info on this wiki page.
The development team tells us: GNUSim8085 is a graphical simulator, assembler and debugger for the Intel 8085 microprocessor in Linux and Windows.
- A simple editor component with syntax highlighting.
- A keypad to input assembly language instructions with appropriate arguments.
- Easy view of register contents.
- Easy view of flag contents.
- Hexadecimal - Decimal converter.
- View of stack, memory and I/O contents.
- Support for breakpoints for program debugging.
- Stepwise program execution.
- One click conversion of assembly program to opcode listing.
- Printing support.
- UI translated in various languages.
[root@desk mythcat]# dnf install gnusim8085.x86_64
...
Installed:
gnusim8085-1.3.7-19.fc30.x86_64 electronics-menu-1.0-21.fc30.noarch
gtksourceview2-2.11.2-27.fc29.x86_64
Complete![mythcat@desk ~]$ gnusim8085The Intel 8085 has seven internal general-purpose 8-bit registers A, B, C, D, E, H, L, and 5 flags — S (sign), Z (zero), AC (Aux Carry), P (Parity) and CY (Carry).
The processor has a total of 246 instructions with which we can manipulate data in the processor registers and memory.
The assembler Intel 8085 mnemonics with the instruction strings, labels define with a named point in the code, the target for JMP or CALL instructions, comments start line with a semicolon ‘;’ is ignored by the assembler and pseudo codes to the assembler that provides some features to the coding process.
For another development assembly tools for hardware, you can find more info on this wiki page.
Posted by
Cătălin George Feștilă
 Labels:
2019,
assembly,
commands,
Fedora 29,
gnusim8085,
linux,
linux tools,
tutorial,
tutorials
Labels:
2019,
assembly,
commands,
Fedora 29,
gnusim8085,
linux,
linux tools,
tutorial,
tutorials
Fedora 30 : Application packages with snap tool.
Snaps are application packages for desktop, cloud, and IoT that are easy to install, secure, cross-platform and dependency-free, see here.
The install of this tool with the dnf install tool is simple:
Let's try with the vlc application:
For example, I try with the qalculate application and not work:
The install of this tool with the dnf install tool is simple:
[root@desk snap]# dnf install snap
...
Installed:
snap-0.6-13.fc29.noarch python2-crypto-2.6.1-25.fc30.x86_64
Complete![mythcat@desk snap]$ sudo ln -s /var/lib/snapd/snap /snap
[mythcat@desk snap]$ snap install snapcraft --classic
snapcraft 3.5 from Canonical✓ installed
[mythcat@desk ~]$ snap help
The snap command lets you install, configure, refresh and remove snaps.
Snaps are packages that work across many different Linux distributions,
enabling secure delivery and operation of the latest apps and utilities.
Usage: snap ...]
Commands can be classified as follows:
Basics: find, info, install, list, remove
...more: refresh, revert, switch, disable, enable
History: changes, tasks, abort, watch
Daemons: services, start, stop, restart, logs
Commands: alias, aliases, unalias, prefer
Configuration: get, set, wait
Account: login, logout, whoami
Permissions: connections, interfaces, interface, connect, disconnect
Snapshots: saved, save, check-snapshot, restore, forget
Other: version, warnings, okay, ack, known
Development: run, pack, try, download, prepare-image
For more information about a command, run 'snap help '.
For a short summary of all commands, run 'snap help --all'.
[mythcat@desk ~]$ snap refresh
All snaps up to date. Let's try with the vlc application:
[mythcat@desk ~]$ snap install vlc
vlc 3.0.6 from VideoLAN✓ installed
[mythcat@desk ~]$ snap run vlc
VLC media player 3.0.6 Vetinari (revision 3.0.6-0-g5803e85)
[00000000019ca3d0] main libvlc: Running vlc with the default interface. Use 'cvlc' to use vlc without interface.
Qt: Session management error: None of the authentication protocols specified are supported
[0000000001a5fae0] main playlist: playlist is empty
QObject::~QObject: Timers cannot be stopped from another threadFor example, I try with the qalculate application and not work:
[mythcat@desk ~]$ sudo snap install qalculate
[sudo] password for mythcat:
snap "qalculate" is already installed, see 'snap help refresh'
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)