Programmed in Ruby and oriented to GNU/Linux systems, but compatible with Windows, MacOS and every systems where Ruby works. It is free, licensed under GNU/GPLv3.
First you need to install the ruby
[root@localhost pentbox]# dnf install ruby
Last metadata expiration check: 1:55:17 ago on Tue Mar 7 20:16:17 2017.
Dependencies resolved.
================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
================================================================================
Installing:
ruby x86_64 2.3.3-61.1.fc25 updates 76 k
ruby-irb noarch 2.3.3-61.1.fc25 updates 94 k
rubygem-bigdecimal x86_64 1.2.8-61.1.fc25 updates 87 k
rubygem-did_you_mean x86_64 1.0.0-61.1.fc25 updates 219 k
rubygem-io-console x86_64 0.4.5-61.1.fc25 updates 57 k
...
rubygems.noarch 2.5.2-61.1.fc25
rubypick.noarch 1.1.1-5.fc24
Complete![root@localhost pentbox]# dnf install svn
Last metadata expiration check: 1:59:41 ago on Tue Mar 7 20:16:17 2017.
Package subversion-1.9.5-1.fc25.x86_64 is already installed, skipping.
Dependencies resolved.
Nothing to do.
Complete!svn co https://pentbox.svn.sourceforge.net/svnroot/pentbox/trunk/ pentbox
cd pentbox
svn update
./pentbox.rb
[root@localhost pentbox]# ./pentbox.rb
PenTBox 1.5
__
U00U|.'@@@@@@`.
|__|(@@@@@@@@@@)
(@@@@@@@@)
`YY~~~~YY'
|| ||
--------- Menu ruby2.3.3 @ x86_64-linux
1- Cryptography tools
2- Network tools
3- Web
4- License and contact
5- Exit
-> 2
1- Net DoS Tester
2- TCP port scanner
3- Honeypot
4- Fuzzer
5- DNS and host gathering
6- MAC address geolocation (samy.pl)
0- Back
-> 3
// Honeypot //
You must run PenTBox with root privileges.
Select option.
1- Fast Auto Configuration
2- Manual Configuration [Advanced Users, more options]
-> 1
HONEYPOT ACTIVATED ON PORT 80 (2017-03-07 22:20:30 +0200)
your_ip:90
INTRUSION ATTEMPT DETECTED! from your_ip:40482 (2017-03-07 22:22:07 +0200)
-----------------------------
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: your_ip
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Fedora; Linux x86_64; rv:51.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/51.0
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Connection: keep-alive
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
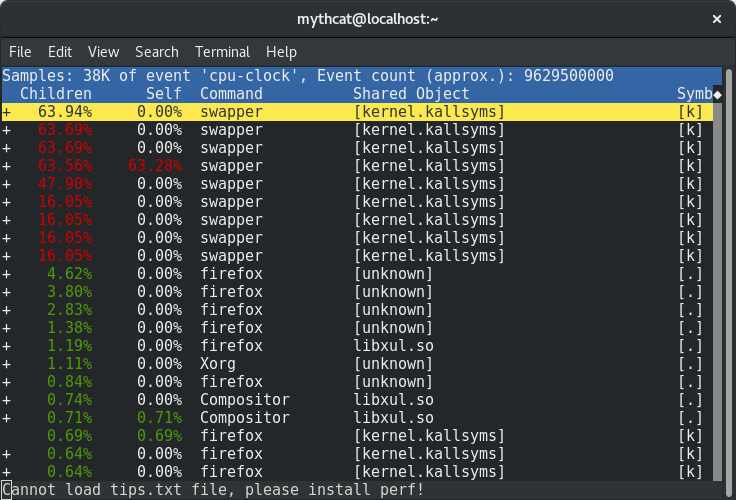 You can use the full list events by using this command:
You can use the full list events by using this command:
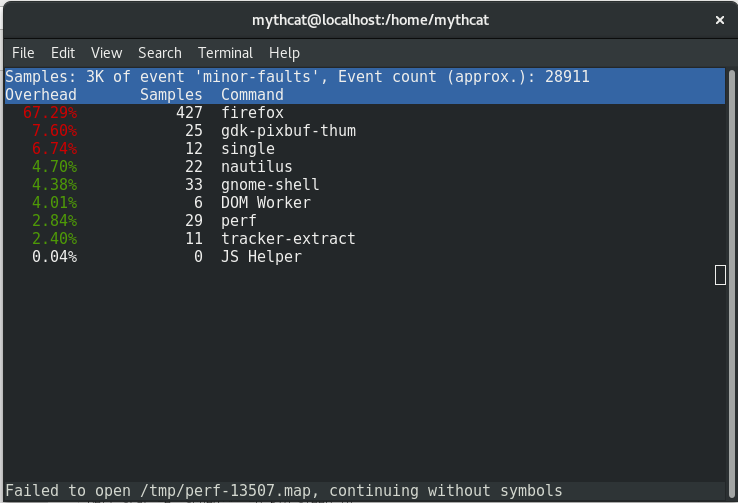 This is most simple way to see how is start and close some pids and how they interact in real-time with the operating system.
Another way to deal with the perf command is how to analyze most scheduler properties from within 'perf sched'
alone using the perf sched with the five sub-commands currently:
This is most simple way to see how is start and close some pids and how they interact in real-time with the operating system.
Another way to deal with the perf command is how to analyze most scheduler properties from within 'perf sched'
alone using the perf sched with the five sub-commands currently: