In this case, I will show how to resize images and preserve aspect ratio:
...with height: 600 pixels
convert -resize x600 *.png convert -resize 600x *.png tutorials, tips, tricks, commands, programming, linux, windows, database, sql, python, programming language, Fedora, drawing, painting, tutorial, tutorials
convert -resize x600 *.png convert -resize 600x *.png From: Linus Torvalds <torvalds <at> linux-foundation.org>
Subject: Linux 3.7
Newsgroups: gmane.linux.kernel
Date: 2012-12-11 03:59:50 GMT (9 hours and 45 minutes ago)
Whee. After an extra rc release, 3.7 is now out. After a few more trials at fixing things, in the end we ended up reverting the kswapd changes that caused problems. And with the extra rc, I had decided to risk doing the buffer.c cleanups that would otherwise have just been marked for stable during the next merge window, and had enough time to fix a few problems that people found there too. There's also a fix for a SCSI driver bug that was exposed by the last-minute workqueue fixes in rc8. Other than that, there's a few networking fixes, and some trivial fixes for sparc and MIPS. Anyway, it's been a somewhat drawn out release despite the 3.7 merge window having otherwise appeared pretty straightforward, and none of the rc's were all that big either. But we're done, and this means that the merge window will close on Christmas eve. Or rather, I'll probably close it a couple of days early. For obvious reasons. It's the main commercial holiday of the year, after all. So aim for winter solstice, and no later. Deal? And even then, I might be deep into the glögg. Linus
Read more here.
# yum install ImageMagick $ convert *.png *.jpg$ mogrify -format png *.jpg $ sudo yum install pv man pv NAME
pv - monitor the progress of data through a pipe
SYNOPSIS
pv [OPTION] [FILE]...
pv [-h|-V]
DESCRIPTION
pv allows a user to see the progress of data through a pipeline, by
giving information such as time elapsed, percentage completed (with
progress bar), current throughput rate, total data transferred, and
ETA.
To use it, insert it in a pipeline between two processes, with the
appropriate options. Its standard input will be passed through to its
standard output and progress will be shown on standard error.
$ pv voronoi.py | python
737B 0:00:00 [86.9kB/s] [==================================>] 100% $ pv /dev/zero > /dev/null
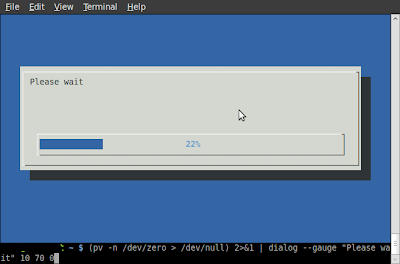
1.1GB 0:00:05 [ 2GB/s] [ <=> ] $ (pv -n /dev/zero > /dev/null) 2>&1 | dialog --gauge "Please wait" 10 70 0
#insmod kernelmoduletest.ko #dmesg | tail $ rmmod kernelmoduletest
ERROR: Removing 'kernelmoduletest': Operation not permitted #include <linux module.h="">
#include <linux kernel.h="">
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("kernelmoduletest");
MODULE_AUTHOR("Catalin George Festila/mythcat/catafest");
int init_module() {
printk(KERN_INFO "Now I will initialize my kernel module\n");
printk(KERN_INFO "Test: Hello World !\n");
return 0;
}
void cleanup_module() {
printk(KERN_INFO "Bad!... kernel module unloaded.\n");
}</linux></linux> obj-m += kernelmoduletest.o
all:
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) clean # make
...
Building modules, stage 2.
MODPOST 1 modules
...
make[1]: Leaving directory `/usr/src/linux-headers-2.6.31-14-generic'
[14694.779227] Now I will initialize my kernel module
[14694.779233] Test: Hello World !
[15049.825605] Bad!... kernel module unloaded. while [ 1 ]; do cat /proc/meminfo; date; echo; sleep 1; done$ watch -d ./meminfo nc -l -p 7000 
nc xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx 7000 


You can execute copies a large block of data to and from disk.
This will minimize disk caching.
Next is one example if our test system has 1GB of RAM.
It is easy ( 1GB = 250,000 blocks ).
$ time sh -c "dd if=/dev/zero of=bigfile bs=8k count=250000 && sync"
250000+0 records in
250000+0 records out
2048000000 bytes (2.0 GB) copied, 37.0113 s, 55.3 MB/s
real 0m40.910s
user 0m0.172s
sys 0m12.641s It's very hard to argue with this dd test.

uvcvideo: Found UVC 1.00 device USB2.0 Camera
mplayer tv:// driver=v4l2:width=640:height=480:device=/dev/video0 -vo null
mplayer tv:// -frames 10 -tv fps=20:driver=v4l2:width=640:height=480:device=/dev/video0 -vo jpeg

