he most important fact in learning development is knowing the information flow and how to drain it knowing the elements and stages of information processing of the content.
That's why I wrote this article succinctly to show you how simple basics of exemplification can correctly complete and help the user to modify and create content.
I will show you how to follow steps into hugo framework and website development with hugo.
You need to read the basic of hugo terms from documentation if you want to learn all about hugo or take some helpful information.
First use
--verbose flag gives extra information that will be helpful when we debug or build your hogo website.
You need to know your hugo version because is the old versions has bad issues, check it with:
$ hugo version
The next command is to see and debug your work:
$ hugo --verbose
How hugo framework works when you start for the first time with hugo development.
Now, the first place that Hugo will look for rules and files is in the
layouts/ directory so it will always find the skin.
If you start with hugo then you can change the default.
This files name skins are the files responsible for the look and feel of your site.
You have two ways to create a skin:
- create it in the layouts/ directory;
- create it in a sub-directory of the themes/ directory.
A skin in
layouts/ folder can’t be customized without updating the templates and static files that it is built from.
The skin created in
themes/ folder , can be and that makes it easier for other people to use it.
In my example tutorial , I add this text to
themes/test_themes_001/layouts/index.html.
The result of running hugo server command will rput this text on your browser at
127.0.0.1:13131, see command:
$ hugo server --buildDrafts
The hugo command come with many features like :
- --buildDrafts this include content marked as draft ( see files with draft:true from .md file);
- --ignoreCache this ignores the cache directory if you use it;
Using
--verbose let you to see your errors.
For example a bad template or configuration can come with this error:
...Unable to locate layout for "taxonomyTerm" ...
This show you what term created by you is not on your hugo development area.
I make just few changes to show you how the hugo working.
First I create the website named
hugo_website_001.
I used hugo command to add some pages
first_test.md and
new.md and a theme named
test_theme_001, see:
$ hugo new site hugo_website_001
$ cd hugo_website_001
$ hugo new theme test_theme_001
$ hugo new first_test.md
$ hugo new new.md
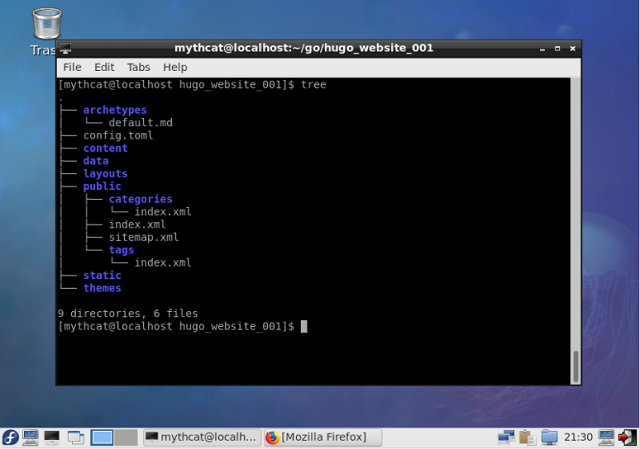
$ tree
.
├── archetypes
│ └── default.md
├── config.toml
├── content
│ ├── first_test.md
│ └── new.md
├── data
├── fpaste_hugo.txt
├── layouts
├── public
│ ├── categories
│ │ └── index.xml
│ ├── css
│ ├── index.html
│ ├── index.xml
│ ├── js
│ ├── sitemap.xml
│ └── tags
│ └── index.xml
├── static
└── themes
└── test_theme_001
├── archetypes
│ └── default.md
├── layouts
│ ├── 404.html
│ ├── _default
│ │ ├── list.html
│ │ └── single.html
│ ├── index.html
│ ├── index.html.save
│ └── partials
│ ├── footer.html
│ └── header.html
├── LICENSE.md
├── static
│ ├── css
│ └── js
└── theme.toml
19 directories, 20 files
$
Let's see files for settings - the toml file type.
First is the
config.toml file:
baseURL = "http://localhost.com"
languageCode = "en-us"
title = "My New Hugo Site"
theme = "test_theme_001"
contentdir ="content"
publishdir = "public"
The next file is the
theme.toml .
# theme.toml template for a Hugo theme
# See https://github.com/gohugoio/hugoThemes#themetoml for an example
name = "Test_theme_001"
license = "MIT"
licenselink = "https://github.com/yourname/yourtheme/blob/master/LICENSE.md"
description = "first theme with hugo"
homepage = "http://example.com/"
tags = ["tags","categories"]
features = []
min_version = "0.31"
[author]
name = "catafest"
homepage = "free-tutorials.org"
# If porting an existing theme
[original]
name = ""
homepage = ""
repo = ""
I will show a minimal example to understand the changes you need to make to run well with hugo framework and the my custom theme.
I show next how this changes into files is show by hugo on browser.
The basic file load is the index.html from
themes/test_theme_001/layouts folder with tag h2 and text
Some text !, see:
Some text !
{{ partial "header.html" . }}
This file load another file from
partials folder and is named
header.html with tag p and this text:
This is a custom header
Let's run the hugo server :
hugo server --theme=test_theme_001 --buildDrafts --ignoreCache --disableFastRender
This is result is this: