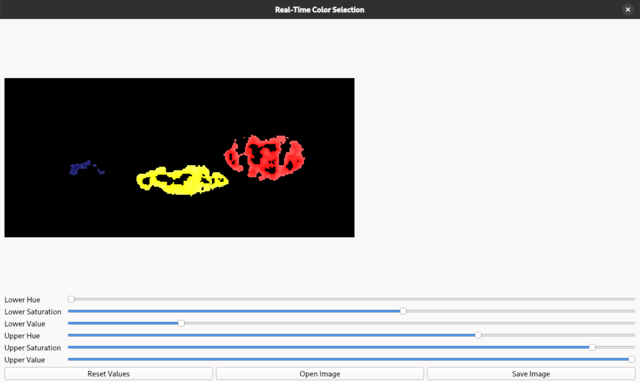
Today I tested another source code with opencv, numpy, PyQt6 python packages.
I install opencv python package with dnf5 tool:
root@localhost:/home/mythcat# dnf5 install python3-opencv.x86_64
The source code let you to open, change a image and save using sliders and a reset option.
This is the source code:
import sys
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QWidget, QVBoxLayout, QLabel, QSlider, QFileDialog, QPushButton, QHBoxLayout
from PyQt6.QtGui import QImage, QPixmap
from PyQt6.QtCore import Qt, pyqtSlot
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("Real-Time Color Selection")
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 1200, 800)
# Create central widget and main layout
central_widget = QWidget()
self.setCentralWidget(central_widget)
main_layout = QVBoxLayout(central_widget)
# Create image label
self.image_label = QLabel()
main_layout.addWidget(self.image_label)
# Initialize sliders
self.lower_h = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Horizontal)
self.lower_s = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Horizontal)
self.lower_v = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Horizontal)
self.upper_h = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Horizontal)
self.upper_s = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Horizontal)
self.upper_v = QSlider(Qt.Orientation.Horizontal)
# Set slider ranges
for slider in [self.lower_h, self.upper_h]:
slider.setRange(0, 179)
for slider in [self.lower_s, self.lower_v, self.upper_s, self.upper_v]:
slider.setRange(0, 255)
# Set initial slider values
self.lower_h.setValue(50)
self.lower_s.setValue(100)
self.lower_v.setValue(50)
self.upper_h.setValue(130)
self.upper_s.setValue(255)
self.upper_v.setValue(255)
# Connect sliders to update function
self.lower_h.valueChanged.connect(self.update_hsv_range)
self.lower_s.valueChanged.connect(self.update_hsv_range)
self.lower_v.valueChanged.connect(self.update_hsv_range)
self.upper_h.valueChanged.connect(self.update_hsv_range)
self.upper_s.valueChanged.connect(self.update_hsv_range)
self.upper_v.valueChanged.connect(self.update_hsv_range)
# Create slider layouts with labels
sliders_layout = QVBoxLayout()
# Add slider pairs with labels
slider_pairs = [
("Lower Hue", self.lower_h),
("Lower Saturation", self.lower_s),
("Lower Value", self.lower_v),
("Upper Hue", self.upper_h),
("Upper Saturation", self.upper_s),
("Upper Value", self.upper_v)
]
for label_text, slider in slider_pairs:
row_layout = QHBoxLayout()
label = QLabel(label_text)
label.setMinimumWidth(120)
row_layout.addWidget(label)
row_layout.addWidget(slider)
sliders_layout.addLayout(row_layout)
main_layout.addLayout(sliders_layout)
# Add buttons
button_layout = QHBoxLayout()
self.reset_button = QPushButton("Reset Values")
self.reset_button.clicked.connect(self.reset_values)
button_layout.addWidget(self.reset_button)
self.open_image_button = QPushButton("Open Image")
self.open_image_button.clicked.connect(self.open_image)
button_layout.addWidget(self.open_image_button)
self.save_button = QPushButton("Save Image")
self.save_button.clicked.connect(self.save_image)
button_layout.addWidget(self.save_button)
main_layout.addLayout(button_layout)
# Process initial image
self.process_image()
def process_image(self):
image_bgr = cv2.imread("image.png")
if image_bgr is None:
image_bgr = cv2.imread("default_image.png")
self.image_bgr = image_bgr
self.image_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(image_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
# Create initial mask using current slider values
lower_values = np.array([self.lower_h.value(), self.lower_s.value(), self.lower_v.value()])
upper_values = np.array([self.upper_h.value(), self.upper_s.value(), self.upper_v.value()])
mask_test = cv2.inRange(self.image_hsv, lower_values, upper_values)
image_bgr_masked = cv2.bitwise_and(image_bgr, image_bgr, mask=mask_test)
self.image_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(image_bgr_masked, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
self.update_image()
def update_image(self):
height, width, channel = self.image_rgb.shape
bytes_per_line = width * channel
q_image = QImage(self.image_rgb.data, width, height, bytes_per_line, QImage.Format.Format_RGB888)
pixmap = QPixmap.fromImage(q_image)
self.image_label.setPixmap(pixmap.scaled(700, 500, Qt.AspectRatioMode.KeepAspectRatio))
def update_hsv_range(self):
lower_values = np.array([self.lower_h.value(), self.lower_s.value(), self.lower_v.value()])
upper_values = np.array([self.upper_h.value(), self.upper_s.value(), self.upper_v.value()])
mask_test = cv2.inRange(self.image_hsv, lower_values, upper_values)
image_bgr_masked = cv2.bitwise_and(self.image_bgr, self.image_bgr, mask=mask_test)
self.image_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(image_bgr_masked, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
self.update_image()
def reset_values(self):
self.lower_h.setValue(50)
self.lower_s.setValue(100)
self.lower_v.setValue(50)
self.upper_h.setValue(130)
self.upper_s.setValue(255)
self.upper_v.setValue(255)
def open_image(self):
filename, _ = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self, "Select Image File", "", "Image Files (*.png *.jpg *.jpeg)")
if filename:
self.image_bgr = cv2.imread(filename)
if self.image_bgr is not None:
self.image_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(self.image_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
self.update_hsv_range() # This will apply current filter and update display
def save_image(self):
filename, _ = QFileDialog.getSaveFileName(self, "Save Image", "", "PNG Files (*.png);;JPEG Files (*.jpg)")
if filename:
# Make sure filename has an extension
if not filename.endswith(('.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg')):
filename += '.png'
# Convert and save
output_image = cv2.cvtColor(self.image_rgb, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
cv2.imwrite(filename, output_image)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())