tutorials, tips, tricks, commands, programming, linux, windows, database, sql, python, programming language, Fedora, drawing, painting, tutorial, tutorials
Wednesday, February 13, 2013
News: Intel and TV service ?
This can be good but can be also an easy way to take some new clients.
The big problem is " What will see in this service?".
I don't expect to see something about the secrets of Intel assembly code or development team, but can be something nice.
Read more here.
Sunday, February 10, 2013
Monday, February 4, 2013
News: DroidCleaner App infects connected PCs
DroidCleaner, an Android app that claims to free up smartphone memory but actually infects connected PCs, has been removed from Google Play but is still available from third-party app stores.
Read more here.
Thursday, January 31, 2013
GNOME Developer Experience Hackfest 2013
This week Red Hat and the GNOME Foundation giving you the chance to attend the Developer Experience hackfest in Brussels.
The goal of the hackfest is to improve the overall application developer experience.
There are three main areas of work we suggest for this hackfest:
- Tooling (Anjuta, Monodevelop, application bundling, intltool, gtk-doc, autofoo and friends...)
- Developer docs and mindshare (unified online/offline API reference UI, app developer community building...)
- Further platform needs (improvement of data-driven apps and other needs with an unclear answer)
- Application bundling and sandboxing, the application as the first class concept in the kernel
Read more about this event here.
Tuesday, January 15, 2013
The linux command: dmidecode
The linux command dmidecode is a tool for dumping a computer's DMI.
# dmidecode -h
Usage: dmidecode [OPTIONS]
Options are:
-d, --dev-mem FILE Read memory from device FILE (default: /dev/mem)
-h, --help Display this help text and exit
-q, --quiet Less verbose output
-s, --string KEYWORD Only display the value of the given DMI string
-t, --type TYPE Only display the entries of given type
-u, --dump Do not decode the entries
-V, --version Display the version and exit Let's see the option: -t.
# dmidecode -t -h
Invalid type keyword: -h
Valid type keywords are:
bios
system
baseboard
chassis
processor
memory
cache
connector
slot Now let's show you some infos about my old processor.
# dmidecode -t processor
# dmidecode 2.9
SMBIOS 2.3 present.
Handle 0x0004, DMI type 4, 32 bytes
Processor Information
Socket Designation: SOCKET A
Type: Central Processor
Family: Other
Manufacturer: AuthenticAMD
ID: 62 06 00 00 FF FB 83 03
Signature: Family 6, Model 6, Stepping 2
Flags:
FPU (Floating-point unit on-chip)
VME (Virtual mode extension)
DE (Debugging extension)
PSE (Page size extension)
TSC (Time stamp counter)
MSR (Model specific registers)
PAE (Physical address extension)
MCE (Machine check exception)
CX8 (CMPXCHG8 instruction supported)
APIC (On-chip APIC hardware supported)
SEP (Fast system call)
MTRR (Memory type range registers)
PGE (Page global enable)
MCA (Machine check architecture)
CMOV (Conditional move instruction supported)
PAT (Page attribute table)
PSE-36 (36-bit page size extension)
MMX (MMX technology supported)
FXSR (Fast floating-point save and restore)
SSE (Streaming SIMD extensions)
Version: AMD Athlon(TM) MP 1700+
Voltage: 1.7 V
External Clock: 133 MHz
Max Speed: 2250 MHz
Current Speed: 1466 MHz
Status: Populated, Enabled
Upgrade: Other
L1 Cache Handle: 0x0009
L2 Cache Handle: 0x000A
L3 Cache Handle: Not Provided
Also you can use this format to read infos.
# dmidecode --type 0 --type 13 The numbers tell what to read, see:
bios
system 1, 12, 15, 23, 32
baseboard 2, 10, 41
chassis 3
processor 4
memory 5, 6, 16, 17
cache 7
connector 8
slot 9 Sunday, January 6, 2013
Deadlock make with Unity - Linux 32 and 64.
Also, the Windows and OSX users can play this game using the web browser with the Unity plugin.
Recommended:
- Intel Core-2-Quad 2.4GHz or similar
- 2 Go Ram
- DX9 3D video card such as Nvidia GTX280 or Radeon HD5850 or newer.Deadlock website
Wednesday, January 2, 2013
Vulnerability? google paypal facebook and internal ip

Do you have any idea about an Internal IP Address or a Private IP Address that too assigned for Multinational Companies? Yeah, today we are gonna discuss about Internal IP or Private IP address Disclosure.
Disclosure of an Internal IP like 192.168.*.* or 172.16.*.* , can really Impact? Most security researchers call it as "bull shit" vulnerability. But when it comes to impact calculation even if the server is behind a firewall or NAT, an attacker can see internal IP of the remote host and this may be used to further attacks.
Read more here.
Linux - Fedora and Android make read-only file system.
After I put my USB cable seam Fedora make from write disk to read-only.
Maybe the Android when scan the device set to read-only.
So you can get some error like this when you use the chown command:
chown: changing ownership of ...: Read-only file system I found a solution, just use remount.
# mount -o rw,remount /media/disk # mount -o ro,remount /media/disk Wednesday, December 26, 2012
News: Tips and tricks: recursive show images
Also: including a screenshot of each project...
This will be the main issue.
... to see the screenshot from each project
...and also to find a way for any file to use
Let's take the book and source code:
$ git clone git://github.com/MasteringOpenCV/code.git code]$ ls
Chapter1_AndroidCartoonifier Chapter7_HeadPoseEstimation
Chapter2_iPhoneAR Chapter8_FaceRecognition
Chapter3_MarkerlessAR Chapter9_FluidInteractionUsingKinect
Chapter4_StructureFromMotion LICENSE.txt
Chapter5_NumberPlateRecognition README.md
Chapter6_NonRigidFaceTracking .
|-- Chapter1_AndroidCartoonifier
| |-- Cartoonifier_Android
| | |-- AndroidManifest.xml
| | |-- jni
| | | |-- Android.mk
| | | |-- Application.mk
| | | `-- jni_part.cpp
| | |-- project.properties
| | |-- res
| | | |-- drawable
| | | | `-- icon.png
| | | `-- values
| | | `-- strings.xml
| | `-- src
| | `-- com
| | `-- Cartoonifier
| | |-- CartoonifierApp.java
| | |-- CartoonifierView.java
| | `-- CartoonifierViewBase.java
| |-- Cartoonifier_Desktop
| | |-- CMakeLists.txt
| | |-- ImageUtils.h
| | |-- ImageUtils_0.7.cpp
| | |-- cartoon.cpp
| | |-- cartoon.h
| | `-- main_desktop.cpp
| |-- README.txt
| `-- screenshot.png
|-- Chapter2_iPhoneAR First, find the screenshot:
code]$ ls -d $PWD/**/*.png
/home/free-tutorials/code/Chapter1_AndroidCartoonifier/screenshot.png
/home/free-tutorials/code/Chapter2_iPhoneAR/screenshot.png
/home/free-tutorials/code/Chapter3_MarkerlessAR/screenshot.png
/home/free-tutorials/code/Chapter4_StructureFromMotion/screenshot.png
/home/free-tutorials/code/Chapter5_NumberPlateRecognition/screenshot.png
/home/free-tutorials/code/Chapter6_NonRigidFaceTracking/screenshot.png
/home/free-tutorials/code/Chapter7_HeadPoseEstimation/screenshot.png
/home/free-tutorials/code/Chapter8_FaceRecognition/screenshot.png
/home/free-tutorials/code/Chapter9_FluidInteractionUsingKinect/screenshot.png code]$ ls -d $PWD/**/*.png | xargs gthumb 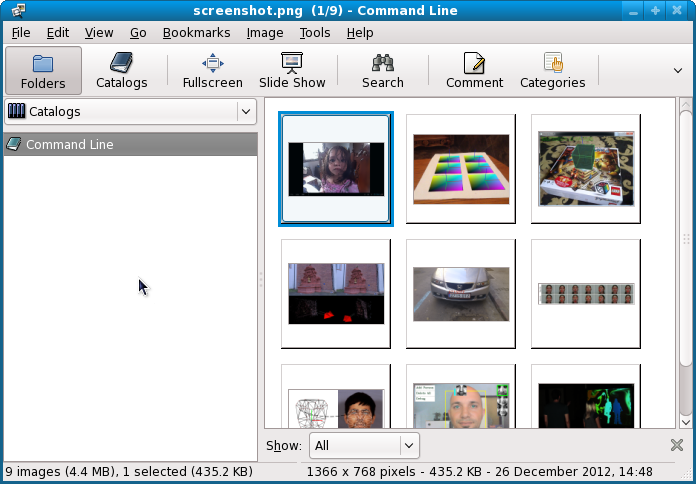
Tuesday, December 18, 2012
ImageMagick resize with preserve aspect ratio.
In this case, I will show how to resize images and preserve aspect ratio:
...with height: 600 pixels
convert -resize x600 *.png convert -resize 600x *.png Tuesday, December 11, 2012
Linus Torvalds - kernel 3.7 is now out.
From: Linus Torvalds <torvalds <at> linux-foundation.org>
Subject: Linux 3.7
Newsgroups: gmane.linux.kernel
Date: 2012-12-11 03:59:50 GMT (9 hours and 45 minutes ago)
Whee. After an extra rc release, 3.7 is now out. After a few more trials at fixing things, in the end we ended up reverting the kswapd changes that caused problems. And with the extra rc, I had decided to risk doing the buffer.c cleanups that would otherwise have just been marked for stable during the next merge window, and had enough time to fix a few problems that people found there too. There's also a fix for a SCSI driver bug that was exposed by the last-minute workqueue fixes in rc8. Other than that, there's a few networking fixes, and some trivial fixes for sparc and MIPS. Anyway, it's been a somewhat drawn out release despite the 3.7 merge window having otherwise appeared pretty straightforward, and none of the rc's were all that big either. But we're done, and this means that the merge window will close on Christmas eve. Or rather, I'll probably close it a couple of days early. For obvious reasons. It's the main commercial holiday of the year, after all. So aim for winter solstice, and no later. Deal? And even then, I might be deep into the glögg. Linus
Read more here.
Monday, December 10, 2012
Simple convert images using ImageMagick - convert features
Install the software under Fedora:
# yum install ImageMagick $ convert *.png *.jpg$ mogrify -format png *.jpg Monday, September 24, 2012
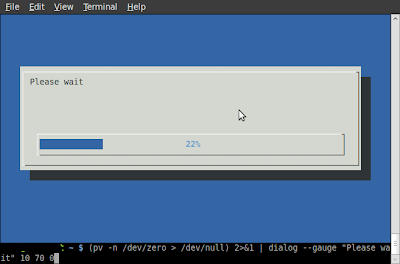
News: Unusual commands in linux : pv
Pipe viewer - pv is a terminal-based tool for monitoring the progress of data through a pipeline written by Andrew Wood
To install pv on Fedora or CentOS do this:
$ sudo yum install pv man pv NAME
pv - monitor the progress of data through a pipe
SYNOPSIS
pv [OPTION] [FILE]...
pv [-h|-V]
DESCRIPTION
pv allows a user to see the progress of data through a pipeline, by
giving information such as time elapsed, percentage completed (with
progress bar), current throughput rate, total data transferred, and
ETA.
To use it, insert it in a pipeline between two processes, with the
appropriate options. Its standard input will be passed through to its
standard output and progress will be shown on standard error.
You can get precise time how long it will take.
$ pv voronoi.py | python
737B 0:00:00 [86.9kB/s] [==================================>] 100% $ pv /dev/zero > /dev/null
1.1GB 0:00:05 [ 2GB/s] [ <=> ] To do this you need to use -n arg.
$ (pv -n /dev/zero > /dev/null) 2>&1 | dialog --gauge "Please wait" 10 70 0